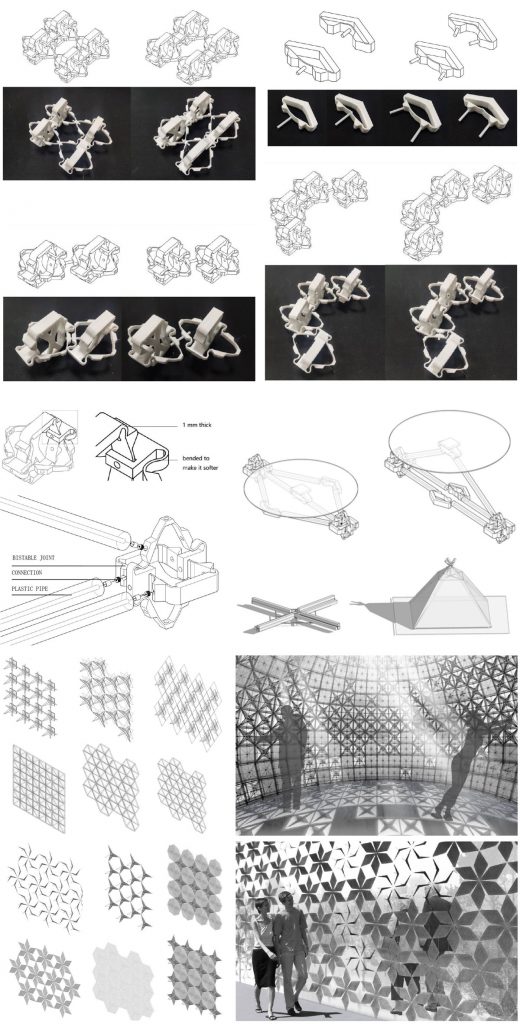
This research investigates the design and fabrication process of an adaptive joint using 3D printed mono-material bistable mechanisms. The proposed joint deforms when external forces are applied, achieving two stable states. An x-shaped microstructure (simulSLE) is designed for the connection portion of the bistable structure inside the joint. 3D-Printing experiments conducted with different materials in this paper, explore the possibility of various forms of simul-SLE itself realizing bistable by a single material, which makes the rigid 3D printed material acquires properties of flexibility and softness. Finally, practical applications are shown how this joint can be used in buildings.
3D Printed Monolithic Joints
SPONSOR
- Nanjing University
COLLABORATORS
- Shiyu Feng (Nanjing University), Mengzeshan du (Nanjing University), Weiyi Wang (Nanjing University), Heng Lu (Nanjing University), Guohua Ji (Nanjing University)
DISSEMINATION
- Feng, Shiyu, Heng Lu, Daekwon Park, 2020. “3D Printed Monolithic Joints: A Mechanically Bistable Joint.” Proceedings of the 25th International Conference of the Association of Computer-Aided Architectural Design Research in Asia (CAADRIA), Bangkok, Thailand