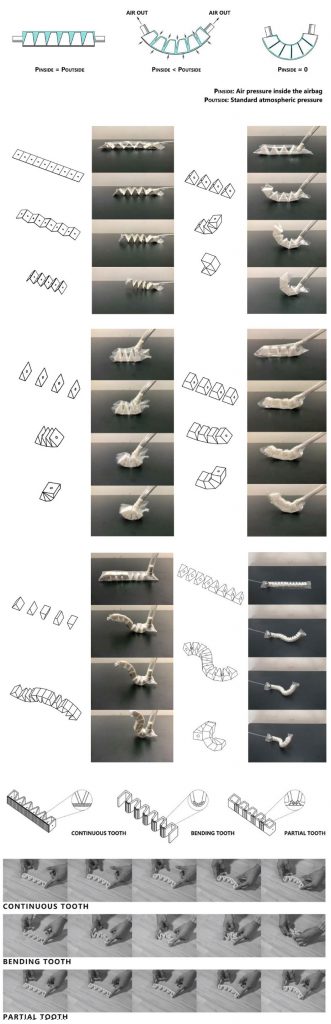
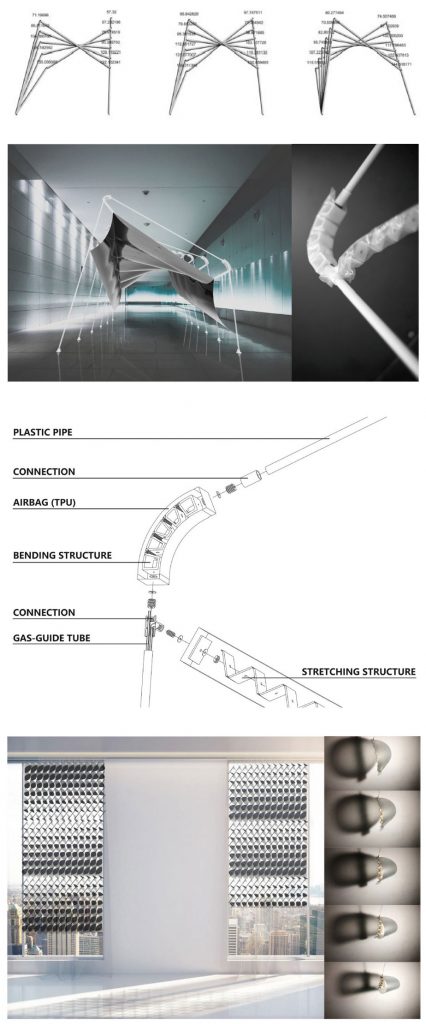
This research investigates the design and fabrication process of an adaptive joint using foldable 3D printed structures encased in heat-sealed synthetic polymer films (e.g. airtight plastic casing). The proposed joint can be pneumatically actuated using the airtight casing, and the shape of the deformation can be controlled using origami-inspired 3D printed structures. A zigzag microstructure is designed for the connection portion of the origami structure inside the joint, in order that the rigid 3D printed material (PLA) acquires properties of mollusk material, such as flexibility and softness. Finally, the paper presents some applications adopting pneumatic origami joints which can interact with people or adapting the indoor environment, and compares
the advantages of this pneumatic technology with mechanical technology.
Pneumatic Origami Joints
SPONSOR
- Nanjing University
COLLABORATORS
- Heng Lu (Nanjing University), Chen Liu (Nanjing University), Guohua Ji (Nanjing University), and Ziyu Tong (Nanjing University)
DISSEMINATION
- Lu, Heng, Daekwon Park, Chen Liu, Guohua Ji, and Ziyu Tong. 2019. “Pneumatic Origami Joints.” In Computer-Aided Architectural Design. “Hello, Culture,” edited by Ji-Hyun Lee, 327–40. Communications in Computer and Information Science. Springer Singapore.
- Lu, Heng, Daekwon Park, Chen Liu, Guohua Ji, and Ziyu Tong. 2019. “Pneumatic Origami Joints.” Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer-Aided Architectural Design Futures (CAAD Futures) 2019, Daejeon, South Korea.